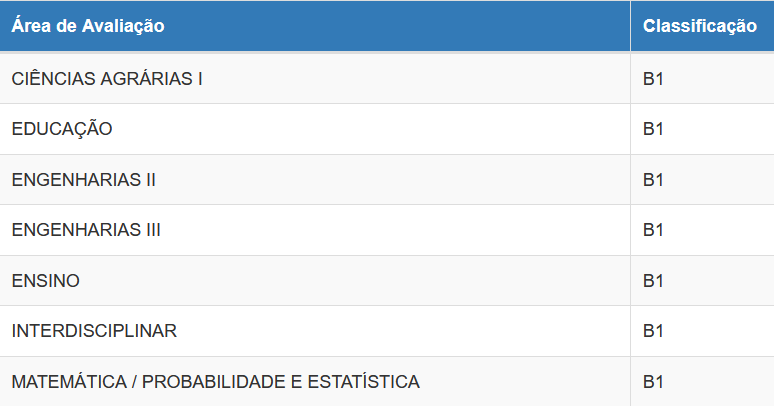
Problem Posing and Solving in Mathematics learning: possibilities for Higher Education
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.35819/remat2021v7iespecialid5513Keywords:
Combinatorial analysis, Computer Science, higher education, remote teaching, computer gamesAbstract
Recent research notes the importance of students developing their role actively in the teaching and learning process. In this sense, this paper aims to analyze the contributions of problem posing and problem solving as teaching conceptions in order to provide higher education students to be active in the development of their learning in Mathematics by posing and solving problems associated with the content of combinatorial analysis. The research took place during the first semester of 2021, developed with 56 students enrolled in two undergraduate Computer Science classes at the Regional University of Blumenau, in Santa Catarina, Brazil. It is characterized as an empirical research, with data of a qualitative-quantitative nature, and with regard to the procedures adopted, it is constituted as an action research, in which data was recorded through a field diary, document registration, and audiovisual recordings. As obtained results, it was analyzed that the conceptions of Mathematics teaching adopted allowed the development of skills associated with mathematical learning, as well as other specific skills related to the students’ own professional training context. However, the research presented possibilities for teaching and learning Mathematics to be investigated in future research and teaching practices, going beyond the exclusive development of mathematical thinking associated with the content covered by allowing students to bring to the classroom their own skills and knowledge, arised from their personal experiences and contexts.
Downloads
References
ALLEVATO, N. S. G.; ONUCHIC, L. R. Ensino-Aprendizagem-Avaliação de Matemática: Por que através da Resolução de Problemas? In: ONUCHIC, L. R.; ALLEVATO, N. S. G.; NOGUTI, F. C. H.; JUSTULIN, A. M. (org). Resolução de problemas: teoria e prática. Jundiaí, SP: Paco Editorial, 2014.
ANDREATTA, C.; ALLEVATO, N. S. G. Aprendizagem matemática através da elaboração de problemas em uma escola comunitária rural. Educação Matemática Debate, Montes Claros, v. 4, n. 10, p. 1-23, 14 abr. 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.24116/emd.e202013.
CAI, J.; HWANG, S. A Perspective for Examining the Link between Problem Posing and Problem Solving. International Group for the Psychology of Mathematics Education, Paderborn, v. 3, p. 103-110, 2003. Disponível em: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED501014.pdf. Acesso em: 20 dez. 2021.
CAI, J.; HWANG, S. Learning to teach through mathematical problem posing: Theoretical considerations, methodology, and directions for future research. Elsevier: International Journal of Educational Research, [s. l.], v. 102, p. 101391, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2019.01.001.
CAI, J.; JIANG, C. An Analysis of Problem-Posing Tasks in Chinese and US Elementary Mathematics Textbooks. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, [s. l.], v. 15, p. 1521-1540, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-016-9758-2.
CAI, J.; MOYER, J. C.; WANG, N.; HWANG, S.; NIE, B.; GARBER, T. Mathematical problem posing as a measure of curricular effect on students' learning. Educational Studies in Mathematics, [s. l.], v. 83, n. 1, p. 57-69, 2013. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-012-9429-3.
CARPES, P. P. G.; CARPES, C. Q. Criar e resolver problemas: habilidades para serem mobilizadas com licenciandos em Matemática. REMAT: Revista Eletrônica da Matemática, Bento Gonçalves, v. 6, n. 2, p. e2008, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.35819/remat2020v6i2id4224.
CRESWELL, J. W.; CLARK, V. L. P. Pesquisa de métodos mistos. 2. ed. Porto Alegre, RS: Penso, 2013.
DEMO, P. Introdução à metodologia da ciência. 2. ed. São Paulo, SP: Atlas, 1985.
DUARTE, E. M. O desenvolvimento de jogos educacionais digitais sob a perspectiva da formulação de problemas e a aprendizagem no ensino superior. Orientadora: Norma Suely Gomes Allevato. 2020. 245 f. Tese (Doutorado em Ensino de Ciências e Matemática) – Universidade Cruzeiro do Sul, São Paulo, 2020.
ECHEVERRÍA, M. P. P.; POZO, J. I. Aprender a Resolver Problemas e Resolver Problemas para Aprender. In: POZO, J. I. (org.). A Solução de Problemas: Aprender a Resolver Problemas e resolver para Aprender. Porto Alegre, RS: Artmed, 1998.
KAUARK, F.; MANHÃES, F. C.; MEDEIROS, C. H. Metodologia da pesquisa: guia prático. Itabuna, BA: Via Litterarum, 2010.
MASOLA, W. J.; ALLEVATO, N. S. G. Dificuldades de aprendizagem Matemática de alunos ingressantes na educação superior. Revista Brasileira de Ensino Superior, Passo Fundo, v. 2, n. 1, p. 64-74, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.18256/2447-3944/rebes.v2n1p64-74.
MORGADO, A. C. O.; CARVALHO, J. B. P.; CARVALHO, B. C. P.; FERNANDEZ, P. Análise combinatória e probabilidade. Rio de Janeiro, RJ: Graftex, 1991.
ONUCHIC, L. R. Ensino-aprendizagem de matemática através da resolução de problemas. In: BICUDO, M. A. V. (org.). Pesquisa em Educação Matemática: Concepções e Perspectivas. São Paulo, SP: Editora UNESP, 1999. p. 199-218.
ONUCHIC, L. R.; LEAL JUNIOR, L. C.; PIRONEL, M. (org.). Perspectivas para Resolução de Problemas. São Paulo: Livraria da Física, 2017.
PACHECO, M. B.; ANDREIS, G. da S. L. Causas das dificuldades de aprendizagem em Matemática: percepção de professores e estudantes do 3º ano do Ensino Médio. Revista Principia, João Pessoa, n. 38, p. 105-119, 2018. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18265/1517-03062015v1n38p105-119.
SCHOENFELD, A. H. Learning to think mathematically: Problem solving, metacognition, and sense-making in mathematics. In: GROUWS, D. A. Handbook for Research on Mathematics Teaching and Learning. New York: MacMillan, 1992.
SCHROEDER, T. L.; LESTER, F. K. Developing understanding in mathematics via problem solving. In: Trafton, P. R.; Shulte, A. P. New directions for elementary school mathematics. Reston: NCTM, 1989.
SILVER, E. A. Problem-posing research in mathematics education: looking back, looking around, and looking ahead. Educational Studies in Mathematics, [s. l.], v. 83, p. 157-162, 2013. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-013-9477-3.
SINGER, F. M., ELLERTON, N.; CAI, J. Problem-posing research in mathematics education: new questions and directions. Educational Studies in Mathematics, [s. l.], v. 83, p. 1-7, 2013. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-013-9478-2.
SINGER, F. M.; ELLERTON, N. F.; CAI, J. Mathematical Problem Posing: From Research to Effective Practice. New York: Springer, 2015.
VAN DE WALLE, J. A. Matemática no Ensino Fundamental: formação de professores e aplicação em sala de aula. 6. ed. Porto Alegre, RS: Artmed, 2009.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 REMAT: Revista Eletrônica da Matemática

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
REMAT retains the copyright of published articles, having the right to first publication of the work, mention of first publication in the journal in other published media and distribution of parts or of the work as a whole in order to promote the magazine.
This is an open access journal, which means that all content is available free of charge, at no cost to the user or his institution. Users are permitted to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search or link the full texts of the articles, or use them for any other legal purpose, without requesting prior permission from the magazine or the author. This statement is in accordance with the BOAI definition of open access.